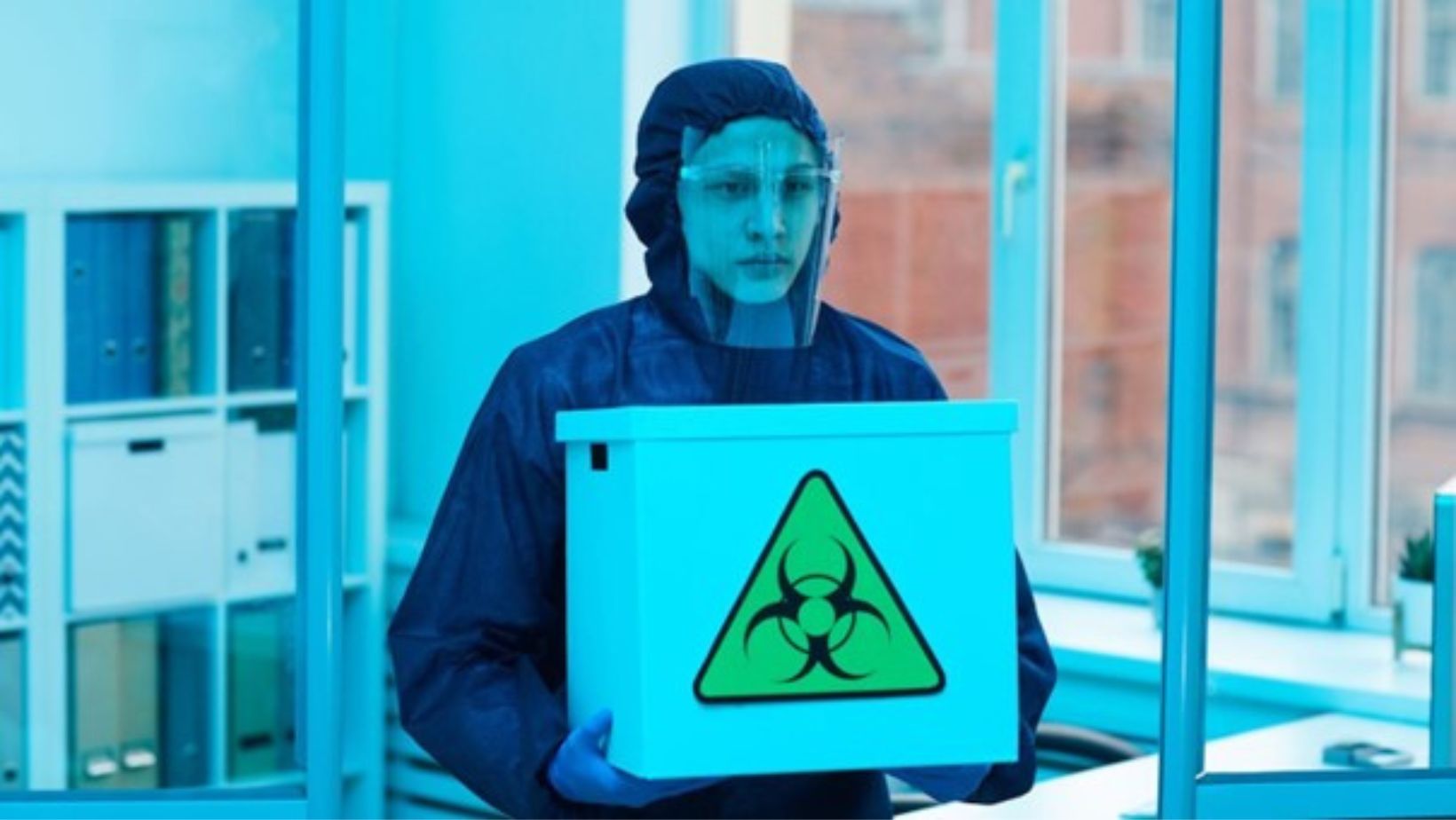
As a business owner or manager who is contemplating using our services, you may have wondered what safety procedures our 40 hour HAZWOPER laborers who are involved in hazardous waste removal need to follow. OSHA HAZWOPER training requirements ensure that all workers are adequately trained to handle hazardous substances safely and effectively. These requirements include specific guidelines on training duration, topics covered, and hands-on practice to ensure compliance and worker safety.
Keep reading this article to get some high-level facts about the HAZWOPER standard and its benefits.
1. What is the HAZWOPER Standard?
The HAZWOPER Standard is a law that requires employers to train their employees about hazardous materials and how to work safely with them.
It was revised in 1994 to become a national standard replacing state or local requirements. The last update to these standards was carried out in 2015.
2. How does it work?
The HAZWOPER standard covers every aspect of managing hazards in your facility, including:
- Identifying hazards in your workplace and reducing their risks
- Training your employees on how to handle those hazards safely
- Provide training for your supervisors on how to ensure that employees are properly trained, as well as how to respond when an accident occurs
 3. What Do I Need to Know About the HAZWOPER Standard?
3. What Do I Need to Know About the HAZWOPER Standard?
There are two parts of the HAZWOPER standard that you should understand before implementing a training program: The first part requires that you develop an emergency action plan (EAP), which includes procedures for responding to emergencies involving hazardous materials or waste;
4. Who Needs the HAZWOPER Training?
The HAZWOPER standard applies to all employees who work at sites where hazardous materials are used or stored—this includes both full-time employees and contractors who arrive on-site for specific jobs only (such as construction workers).
It also applies regardless of whether these workers are wearing protective equipment like respirators or overalls when they’re working with hazardous materials; or if they’re exposed at all during their shift.
 5. Employers Must Provide Training
5. Employers Must Provide Training
In accordance with 29 CFR 1910 Subpart Z within 10 days of an employee’s first exposure to a hazardous substance at work or when an employee is assigned a new task involving exposure to a hazardous substance (see 29 CFR 1910 Subpart Z).
Conclusion
In the end, when it comes to HAZWOPER training, employers are responsible for ensuring their workers are trained in accordance with OSHA guidelines. While there are many institutions that help by providing this training, it is ultimately the employer who is responsible for ensuring the proper people receive the proper training.
 3. What Do I Need to Know About the HAZWOPER Standard?
3. What Do I Need to Know About the HAZWOPER Standard? 5. Employers Must Provide Training
5. Employers Must Provide Training